Market Intelligence: Geographic Risk Factors for Treatment Non-Adherence

Why do identical therapies achieve vastly different real-world effectiveness across congressional districts? The answer lies in understanding how geographic, economic, and social risk factors impact patient treatment follow-through rates.
Pharmaceutical companies invest billions in developing effective treatments, yet real-world outcomes vary dramatically based on patient location. While clinical trials demonstrate drug efficacy under controlled conditions, post-market surveillance reveals that treatment adherence and completion rates can differ by 30-50% between urban, suburban, and rural markets. By analyzing risk factor profiles across Pennsylvania’s three distinct congressional districts—from the 3rd District’s urban Philadelphia core (Rep. Dwight Evans) to the 6th District’s Chester County suburbs (Rep. Chrissy Houlahan) to the 15th District’s rural Appalachian communities (Rep. Glenn Thompson)—we can identify predictive indicators that help pharmaceutical companies optimize market access strategies, patient support programs, and provider engagement initiatives across diverse therapeutic areas.
Urban Markets: Complex Adherence Challenges in High-Density Populations
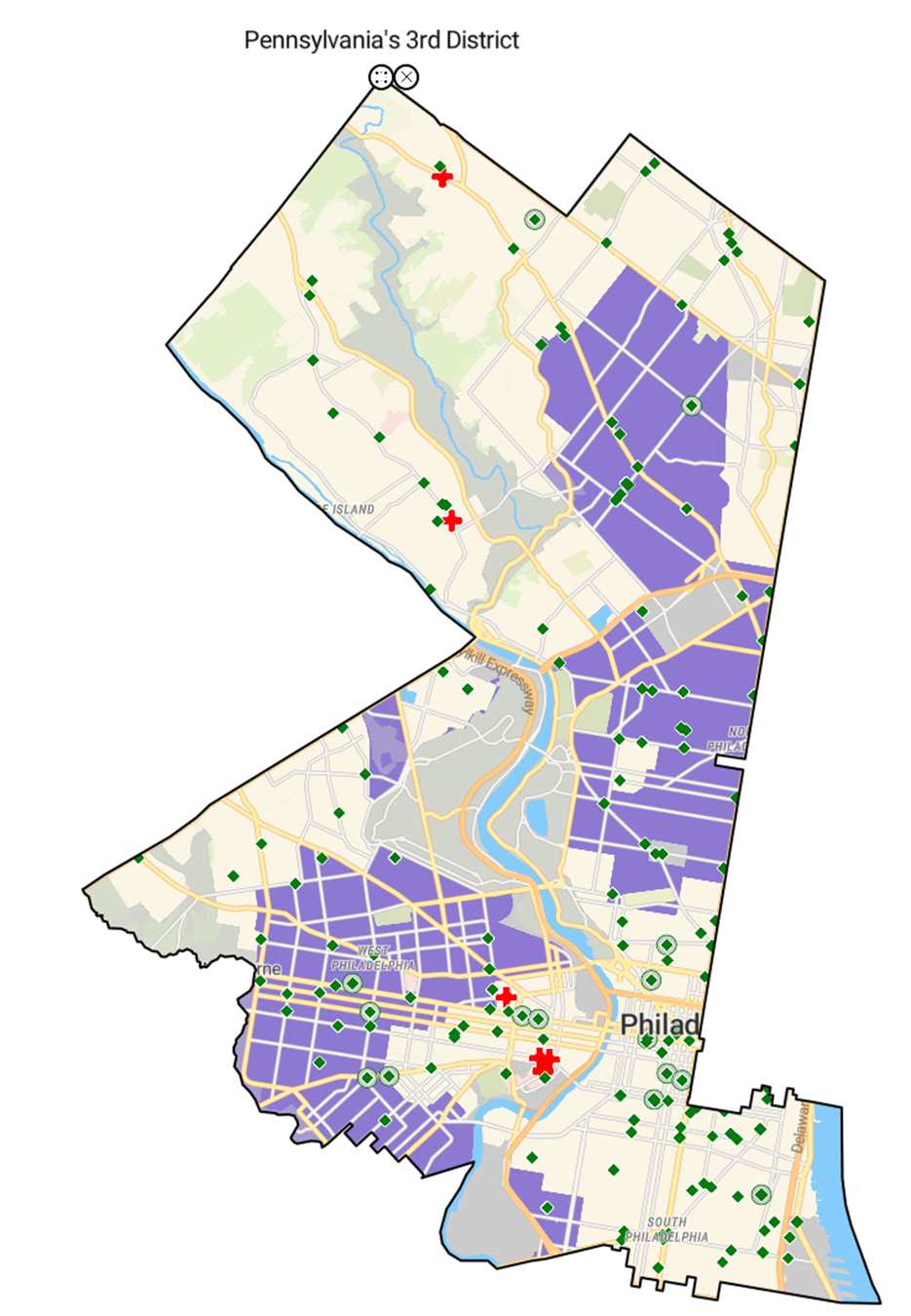
Congressional District Analysis: Pennsylvania’s 3rd District (Rep. Dwight Evans) Includes Center City, West Philadelphia, and North Philadelphia
Urban pharmaceutical markets present a complex therapeutic challenge where environmental factors, socioeconomic barriers, and health behaviors create cascading adherence risks. Pennsylvania’s 3rd congressional district reveals how asthma treatment and smoking cessation therapies face systematic barriers in communities that need them most.
Geographic Risk Clustering:
- Asthma prevalence: Over 10% of residents
- Racial demographics: 50% or higher Black population
- Economic vulnerability: Household income $80,000 or less
- Healthcare access: Federally designated Medically Underserved Areas
- Smoking prevalence: 10% or more current smokers
Key Risk Indicators:
- Elevated Asthma Burden with Poor Management: West Philadelphia and North Philadelphia show asthma rates exceeding 10%—significantly above national averages—yet these same communities face the greatest barriers to consistent controller medication use due to cost, pharmacy access, and fragmented care
- Environmental Amplification of Respiratory Risk: Areas with 50%+ Black population and household incomes under $80,000 experience disproportionate air pollution exposure from industrial sources and traffic corridors, creating environments that both trigger asthma symptoms and undermine treatment effectiveness
- Smoking Addiction in High-Risk Populations: Communities with smoking rates above 10% face dual challenges—higher likelihood of tobacco addiction initiation due to stress and environmental factors, combined with reduced access to cessation resources and medications
- Healthcare Infrastructure Mismatch: Major hospitals concentrate in Center City and South Philadelphia, while Medically Underserved Areas align with neighborhoods experiencing the highest respiratory disease burden and smoking rates
- Cascading Pharmacy Access Crisis: Recent chain closures and SEPTA service cuts eliminate medication access points precisely where residents need consistent access to inhalers, controller medications, and smoking cessation therapies
Market Implications: The geographic concentration of respiratory health risks creates a perfect storm for treatment non-adherence in asthma and smoking cessation therapies. Patients in West and North Philadelphia are more likely to develop asthma, less likely to maintain controller medication regimens, more susceptible to smoking addiction, and less likely to successfully quit—all while living in environments with poor air quality that exacerbate respiratory conditions. Pharmaceutical companies must recognize that traditional adherence strategies will fail without addressing the environmental and structural factors that drive both disease burden and treatment barriers in these communities.
Suburban Markets: The “Adherence Advantage” Zone
Congressional District Analysis: Pennsylvania’s 6th District (Rep. Chrissy Houlahan) Includes Chester County and the City of Reading
Suburban pharmaceutical markets represent the optimal environment for treatment adherence, combining financial stability, healthcare access, and preventive care engagement. Pennsylvania’s 6th congressional district demonstrates how multiple protective factors converge to create ideal conditions for successful treatment completion across therapeutic areas.
Geographic Advantage Indicators:
- Insurance coverage: 93% or higher with health insurance
- Economic stability: Household income $80,000 or more
- Health outcomes: Life expectancy 77 years or higher
- Preventive care engagement: 75% receive annual checkups
- Healthcare investment: Average $1,000+ per person in annual medical spending
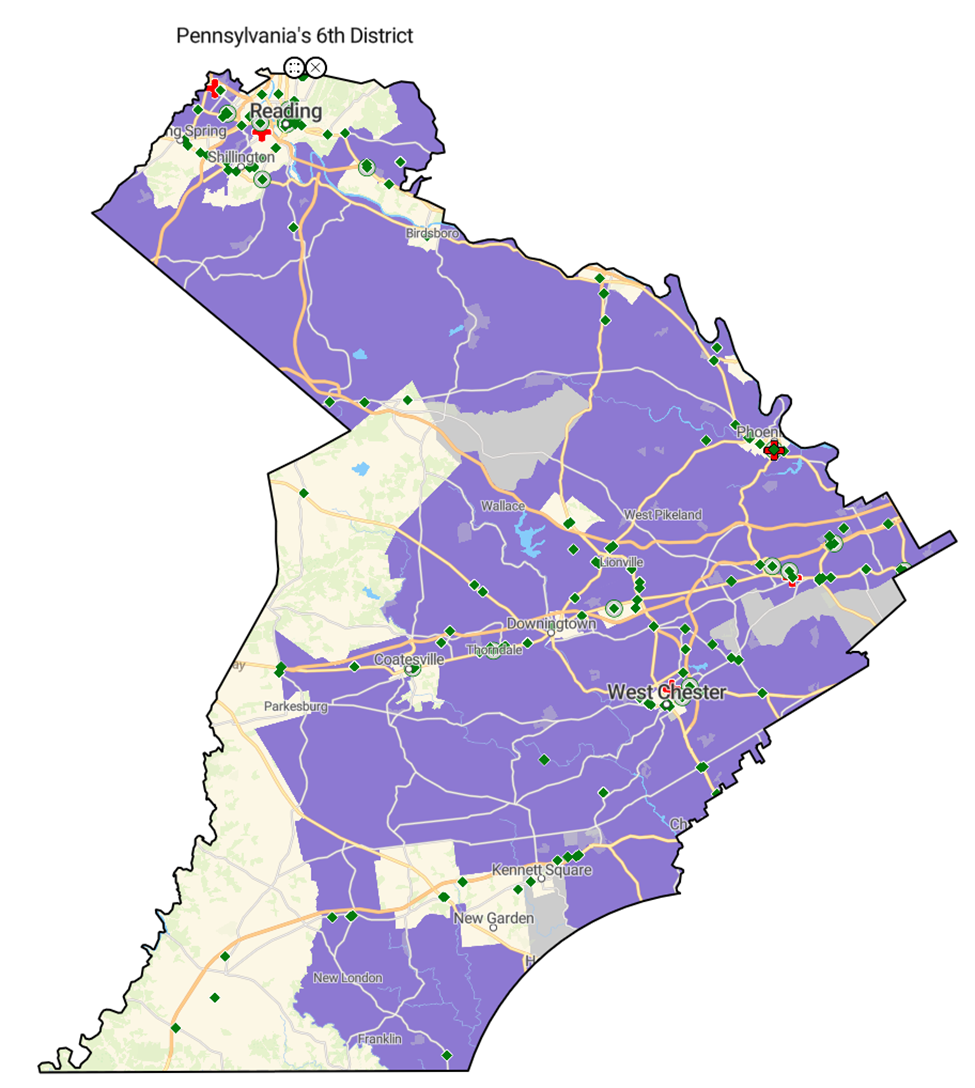
Market Implications: The vast majority of Pennsylvania’s 6th district creates the most reliable adherence environment for pharmaceutical companies. Extensive suburban communities throughout Chester County demonstrate exceptional adherence potential—high insurance coverage rates eliminate most financial barriers to prescription access, while stable household incomes above $80,000 support consistent medication purchasing and specialist care. Universal vehicle ownership eliminates transportation barriers, and no areas face medical underservice or access limitations.
However, smaller urban centers like West Chester, Reading, Coatesville, Parkesburg, Downingtown, and Kennett Square, along with scattered rural communities outside the suburban core, do not consistently meet these optimal criteria. These pockets represent traditional adherence challenges within an otherwise advantageous market environment.
The district’s 75% annual checkup rate indicates strong patient-provider relationships that facilitate treatment monitoring and adjustment across suburban areas. Combined with $1,000+ per capita medical spending and life expectancies of 77+ years, the dominant suburban population represents patients who actively invest in their health outcomes. Pharmaceutical companies can implement premium pricing strategies, introduce complex treatment regimens, and rely on provider-driven adoption rather than intensive patient assistance programs. This market segment justifies investment in clinical decision support tools and provider education initiatives that leverage the existing healthcare engagement infrastructure, while requiring minimal targeted interventions for the small urban exceptions.
Rural Markets: Infrastructure Barriers to Treatment Success
Congressional District Analysis: Pennsylvania’s 15th District (Rep. Glenn Thompson) Includes rural Appalachian Pennsylvania communities
Rural pharmaceutical markets face unique adherence challenges stemming from provider shortages, distance barriers, and limited healthcare infrastructure. Pennsylvania’s 15th congressional district reveals how geographic isolation creates systematic barriers to cancer care initiation and treatment completion, particularly for colorectal cancer therapies.
Geographic Risk Clustering:
- Colorectal cancer burden: 33 or more cases per 100,000 population
- Screening gaps: 30% or more of people over 45 do not receive colorectal screening
- Provider shortage: Federally designated Health Professional Shortage Areas
- Surgical capacity: 1 or fewer colorectal surgeons per 100,000 population
- Elderly population: 8% or more of residents on Medicare
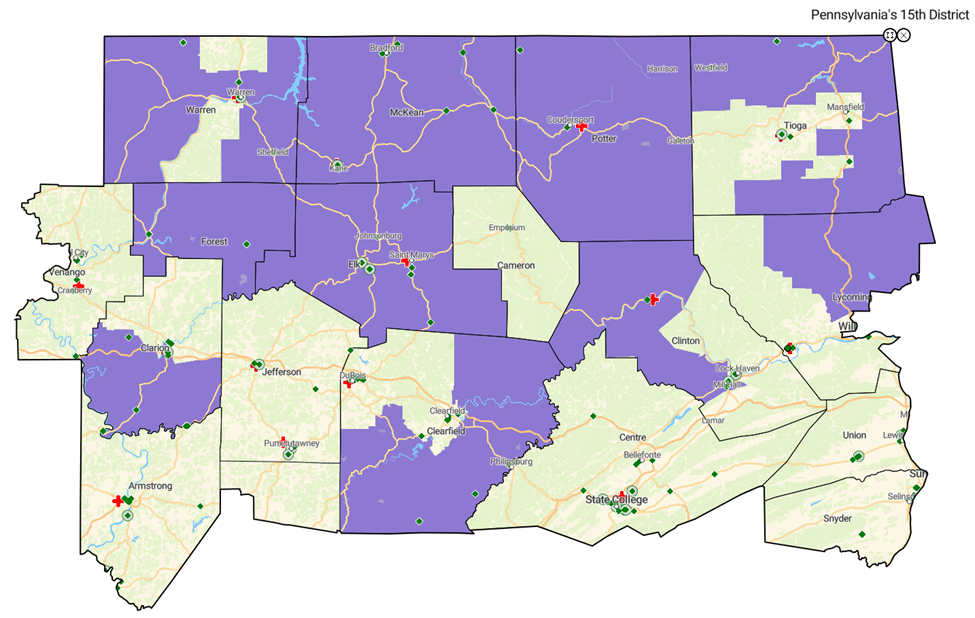
Market Implications: Rural Pennsylvania’s 15th district presents pharmaceutical companies’ most challenging adherence environment for oncology treatments. Counties meeting these high-risk criteria typically have only 1 or no hospitals and limited pharmacy presence, creating fundamental barriers to both cancer detection and treatment continuity. While counties with larger towns or proximity to cities like Pittsburgh are less likely to meet these criteria, the isolated rural communities face compounded disadvantages.
Elderly rural populations in these high-risk areas are least likely to receive screening that enables early cancer detection, most likely to face delayed treatment initiation due to provider shortages, and most vulnerable to treatment discontinuation due to travel burdens and limited support infrastructure. With only 1 or fewer colorectal surgeons per 100,000 residents and some counties served by just a few pharmacies, patients may travel hours for initial diagnosis and ongoing care. This market requires innovative delivery models including telemedicine integration, mobile oncology services, and enhanced patient navigation programs that address both medical complexity and geographic isolation. Traditional adherence strategies fail without addressing the fundamental infrastructure gaps that prevent treatment access in the first place.
Integrated Risk Assessment Framework
Predictive Modeling for Treatment Adherence Across Therapeutic Areas
By mapping these geographic risk factors across Pennsylvania’s diverse congressional districts, pharmaceutical companies can develop predictive models for treatment follow-through likelihood across multiple therapeutic areas—from respiratory therapies in urban environments to preventive care in suburban markets to oncology treatments in rural settings.
High-Risk Indicators (Increased Non-Adherence Probability):
- Respiratory Health Markets: Asthma >10% + smoking >10% + environmental pollution exposure + pharmacy desert conditions
- Cancer Care Markets: Limited screening uptake (30%+ non-adherent) + surgical specialist shortage (<1 per 100K) + elderly population concentration (8%+ Medicare)
- Cross-Therapeutic Barriers: Medically Underserved Area designation + household income <$80K + transportation dependency + limited hospital access
Protective Factors (Improved Adherence Probability):
- Suburban Advantage Clustering: 93%+ insurance coverage + $80K+ household income + 75%+ annual checkup rates + universal vehicle access
- Healthcare Infrastructure Density: Multiple provider options + pharmacy accessibility + hospital proximity
- Preventive Care Engagement: $1K+ per capita medical spending + life expectancy 77+ years
Therapeutic-Specific Risk Stratification:
- Asthma/COPD Therapies: Highest risk in urban areas with environmental triggers and fragmented care
- Smoking Cessation Programs: Most challenging in communities with >10% smoking rates and socioeconomic stress factors
- Cancer Treatments: Greatest barriers in rural areas are a lack of surgical specialists and screening infrastructure
- Chronic Disease Management: Optimal outcomes in suburban markets with established provider relationships
Strategic Applications for Pharmaceutical Companies
Market Access and Pricing Strategy: Use geographic risk profiles to inform differential pricing approaches—premium strategies for suburban markets (PA-6) with high adherence probability, value-based contracts for urban markets (PA-3) requiring intensive support, and innovative access models for rural markets (PA-15) with infrastructure constraints.
Therapeutic Area Prioritization: Align commercial investments with geographic market readiness. Suburban markets support complex oncology regimens and specialty therapies, urban markets require respiratory health focus with robust patient support, while rural markets need telemedicine-enabled chronic disease management solutions.
Provider Engagement Strategy: Deploy specialized sales teams for high-risk areas requiring enhanced clinical support (PA-3 respiratory specialists, PA-15 oncology navigation), while leveraging traditional provider education models in adherence-advantaged suburban markets (PA-6).
Patient Support Program Design: Develop location-specific interventions—environmental health and pharmacy access solutions for urban respiratory patients, care coordination and transportation support for rural cancer patients, and provider-driven monitoring tools for suburban chronic disease management.
Real-World Evidence Generation: Incorporate geographic and therapeutic-specific risk factors into post-market studies to demonstrate treatment effectiveness across diverse patient populations and justify differential support program investments.
Commercial Resource Allocation: Scale field force deployment and marketing investments based on adherence probability models rather than simple population density—intensive support for high-need/high-barrier markets, efficiency-focused approaches for adherence-advantaged markets.
The Bottom Line
Geographic location and therapeutic area intersect to create predictable patterns of treatment adherence success. Pharmaceutical companies that integrate place-based risk assessment with therapy-specific considerations can optimize resource allocation, improve patient outcomes, and enhance real-world treatment effectiveness across Pennsylvania’s diverse congressional districts—from urban respiratory challenges to suburban chronic disease opportunities to rural oncology barriers. This framework transforms geographic data into actionable business intelligence that drives both commercial success and improved patient outcomes across diverse therapeutic areas.
Request More Information
Pharmaceutical companies can leverage PolicyMap’s geographic data to uncover these patterns with precision. Use PolicyMap to inform market access strategies, target patient support programs, and engage providers where adherence risks are highest.